The market is crowded with peppermint oil and as consumers opt for plant-based ingredients, there is an incentive to market products as 100% natural in an effort to stand out on a competitive basis. Despite label claims, peppermint essential oils may not be comprised wholly of raw material.
As peppermint oil prices rise, economically motivated adulteration is a major issue. Fraudulent, synthetic ingredients are intentionally added to products in order to reduce the cost of production or increase the apparent value for the overall purpose of economic gain.1
In order to provide clarity within the essential oils industry, this article focuses on a peppermint oil case study and the application of carbon-14 testing to authenticate naturally sourced ingredients while at the same time, screening samples for potential adulteration.
How carbon-14 detects synthetic substances
Carbon-14 testing is vital to provide analytical evidence of the source of an ingredient. When testing essential oils, the analysis determines whether an essential oil is comprised of renewable or petrochemical-derived sources and therefore can verify if an essential oil has undergone adulteration.
Materials originating from nature have a known radiocarbon level, whereas petroleum-derived material has no radiocarbon left. Therefore, using carbon-14 to analyze a product solely derived from renewable origins, such as plant or animal sources, yields results of 100% biobased. In contrast, a product that is a blend of natural extract and synthetic additives will yield a result between 0% and 100% biobased.2
Analyzing peppermint oil
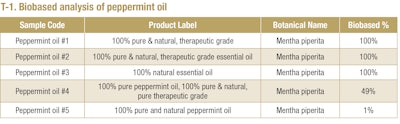
Natural product testing laboratory, Beta Analytic, performed a case study on five peppermint oil samples to identify the presence of any fraudulent “natural” oil in the marketplace (see T-1). Each one-ounce sample was purchased from a major online platform with prices ranging from USD $4.99 to USD $14.98. The labels on all five samples claimed them as “100% natural” peppermint oil.
Through the application of carbon-14 analysis, adulteration of natural-labeled peppermint oil was revealed.
Peppermint oil #1, #2 and #3 yielded results of 100% biobased, authenticating their label claims through analytical evidence of wholly plant-based origin.
As the popularity of peppermint oil grows, the global market for peppermint oil is forecasted to reach USD $671 million by the end of 2022.6
In contrast, analysis of peppermint oil #4 and peppermint oil #5 indicated evidence of synthetic sources. Peppermint oil #4 was comprised of 49% biobased carbon content, demonstrating the peppermint oil was comprised of natural extract blended with petrochemical-derived material. Peppermint oil #5 yielded results of 1% biobased carbon, and therefore, in stark contrast to its label, was almost entirely derived from synthetic substances.
More on the popularity of peppermint oil
Peppermint oil is in high demand as the essential oil is used in several areas, for example, aromatherapy and therapeutic, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, oral care and food and beverage flavoring.
Serving as a therapeutic agent, peppermint oil contributes to the lucrative growth the aromatherapy market is experiencing. Peppermint oil is favored not only for its calming effect but also for its natural healing benefits: anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea, digestive and decongestant properties.3
Contributing to its demand, peppermint oil aromatherapy is reported to increase concentration and cognitive performance, acting at times as a treatment for attention deficits.4 In 2008, a clinical study tested the effect of peppermint oil versus ylang-ylang aromas on cognitive performance among one hundred forty-four healthy participants. Data revealed that peppermint aromatherapy enhanced memory and increased alertness, while ylang-ylang did the opposite.5
The rise in demand for natural aromatherapy treatments is a key driver of the peppermint oil market. As the popularity of peppermint oil grows, the global market for peppermint oil is forecasted to reach USD $671 million by the end of 2022.6

Challenges within the peppermint market
Several farms within the United States, India and China are designated for peppermint production. Once harvested, peppermint is often prepared by steam distillation. This process is necessary to produce peppermint oil by extracting oil from Mentha piperita.7
Within the global landscape, the United States dominates both production and exportation of peppermint oil, and within the country, the peppermint industry is the largest commercial herb industry.8 Although demand for peppermint oil is increasing, both the number of available acres to grow peppermint and the quantity of peppermint produced are slightly decreasing.
In 2015, 65,300 acres of land in the United States was harvested for peppermint with an output of about 5.88 million pounds of peppermint oil. In 2017, 60,400 acres of land were designated for peppermint production, yielding approximately 5.77 million pounds of peppermint oil.9
Growers are faced with challenges due to less available production land for peppermint as corn production takes over land. Large quantities of raw material are required to produce substantial amounts of essential oil. For example, one acre of mint produces about 70 pounds of peppermint oil.10 With decreasing available land and therefore less raw material, there is a spike in the price of peppermint oil for consumers.
Synthetic menthol is replacing natural peppermint due to price fluctuations as high as 150%.11 This leads manufacturers to consider other options to satisfy consumer demand, such as the production of peppermint oil comprised of cheaper synthetic adulterants.
Conclusion
Although it is common to encounter peppermint oil products labeled as “100% natural,” the peppermint oil market is vulnerable to adulteration as ingredients are not always consistent with label claims. The economically motivated adulteration of natural ingredients with synthetic additives can occur because of the combination of increasingly limited peppermint farmland in addition to expensive prices within the commodity’s market. Carbon-14 testing is therefore crucial, acting as a key tool to screen “natural” peppermint oil for petrochemical-derived components.